Molecule Tutorials - Herong's Tutorial Examples - v1.26, by Herong Yang
DNA Gene Sequence - Exons and Introns
This section provides a quick introduction of the Genetic Translation process, which is the process of translating the nucleotide sequence of a mRNA (Messenger RNA) into the amino acid sequence linked with peptide bonds to build a new protein according to the genome codon map chart.
A gene stored in a DNA actually has two types of segments:
- Exon - A segment of nucleotides that gets transcribed to the mRNA to code for proteins in the gene expression process.
- Intron - A segment of nucleotides that is not transcribed to the mRNA and is not used in the gene expression process.
The diagram (source: biotechprimer.com) below shows how introns are removed during the alternative splicing step:
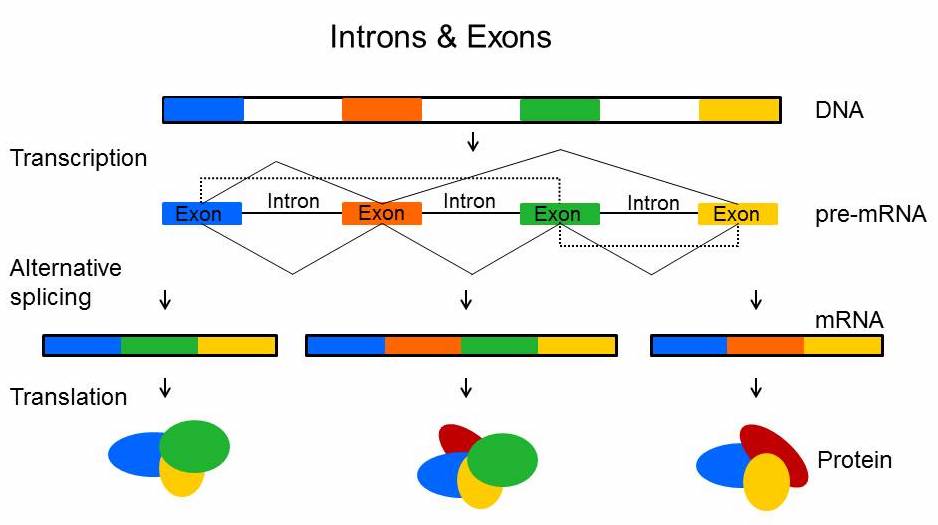
Here is a list of multiples of exons and introns representing a full genomic DNA sequence, which is mapped to its coding DNA (or mRNA) sequence, and its protein sequence.

Table of Contents
Molecule Names and Identifications
Nucleobase, Nucleoside, Nucleotide, DNA and RNA
Gene Expression - Building Proteins
Genetic Transcription - Creating mRNA
Genetic Translation - Creating Protein
►DNA Gene Sequence - Exons and Introns
Chromosome Replication (or DNA Replication)
ChEMBL Database - European Molecular Biology Laboratory
PubChem Database - National Library of Medicine
INSDC (International Nucleotide Sequence Database Collaboration)
HGNC (HUGO Gene Nomenclature Committee)