MySQL Tutorials - Herong's Tutorial Examples - v4.46, by Herong Yang
What Are Storage Engines
This section describes MySQL storage engines, which implement different strategies on how data is stored, updated and retrieved in storage devices.
What Are Storage Engines - Storage Engines are pluggable modules in MySQL Server that implement different strategies on how data is stored, updated and retrieved in storage devices.
As of MySQL Server 8, the following Storage Engines are supported:
1. InnoDB: A transaction-safe (ACID compliant) storage engine for MySQL that has commit, rollback, and crash-recovery capabilities to protect user data. InnoDB row-level locking (without escalation to coarser granularity locks) and Oracle-style consistent nonlocking reads increase multi-user concurrency and performance. InnoDB stores user data in clustered indexes to reduce I/O for common queries based on primary keys. To maintain data integrity, InnoDB also supports FOREIGN KEY referential-integrity constraints.
2. MyISAM: A light, non-transactional engine with great performance and a small data footprint, It is based on ISAM (Indexed Sequential Access Method), an indexing algorithm developed by IBM that allows retrieving information from large sets of data in a fast way.
3. MEMORY (formerly known as HEAP): It creates special-purpose tables with contents that are stored in memory.
4. CSV: The CSV storage engine stores data in text files using comma-separated values format.
5. ARCHIVE: It provides the perfect solution for storing and retrieving large amounts of seldom-referenced historical, archived, or security audit information.
6. BLACKHOLE: The BLACKHOLE storage engine acts as a “black hole” that accepts data but throws it away and does not store it. Retrievals always return an empty result.
7. NDB (also known as NDBCLUSTER): The NDB storage engine is particularly suited for applications that require the highest possible degree of uptime and availability.
8. MERGE (also known as the MRG_MyISAM): A collection of identical MyISAM tables that can be used as one. “Identical” means that all tables have identical column data types and index information.
9. FEDERATED: Lets you access data from a remote MySQL database without using replication or cluster technology. Querying a local FEDERATED table automatically pulls the data from the remote (federated) tables. No data is stored on the local tables.
10. EXAMPLE: A stub engine that does nothing. Its purpose is to serve as an example in the MySQL source code that illustrates how to begin writing new storage engines. As such, it is primarily of interest to developers.
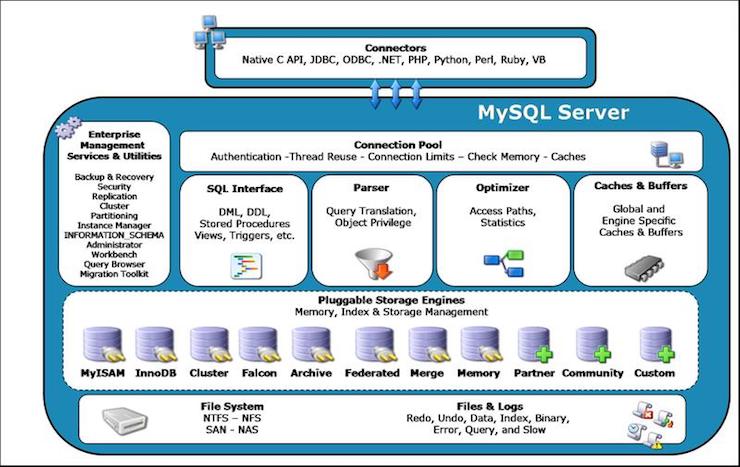
The MySQL server architecture provides a standard set of management and support services that are common among all underlying pluggable storage engines. The storage engines themselves are the components of the database server that actually perform actions on the underlying data that is maintained at the physical server level.
The picture below shows you how pluggable storage engines are integrated in the MySQL server architecture.
The table below provides a comparison of feature availabilities in several major storage engines:
Feature MyISAM Memory InnoDB Archive NDB ------- ------ ------ ------ ------- --- B-tree indexes Yes Yes Yes No No Backup/point-in-time recovery Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Cluster database support No No No No Yes Clustered indexes No No Yes No No Compressed data Yes No Yes Yes No Data caches No N/A Yes No Yes Encrypted data Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Foreign key support No No Yes No Yes Full-text search indexes Yes No Yes No No Geospatial data type support Yes No Yes Yes Yes Geospatial indexing support Yes No Yes No No Hash indexes No Yes No No Yes Index caches Yes N/A Yes No Yes Locking granularity Table Table Row Row Row MVCC No No Yes No No Replication support Yes Limited Yes Yes Yes Storage limits 256TB RAM 64TB None 384EB T-tree indexes No No No No Yes Transactions No No Yes No Yes Upd. stats for data dictionary Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes
You can use the "SHOW ENGINES" statement to see which storage engines are supported in your MySQL server:
mysql> select @@version; @@version --------- 8.0.21 mysql> show engines; Engine Support Comment ---------- ------- -------------------------------------------------------------- FEDERATED NO Federated MySQL storage engine MEMORY YES Hash based, stored in memory, useful for temporary tables InnoDB DEFAULT Supports transactions, row-level locking, and foreign keys MyISAM YES MyISAM storage engine MRG_MYISAM YES Collection of identical MyISAM tables BLACKHOLE YES /dev/null storage engine (anything you write to it disappears) CSV YES CSV storage engine ARCHIVE YES Archive storage engine
Table of Contents
MySQL Introduction and Installation
Introduction of MySQL Programs
Perl Programs and MySQL Servers
Java Programs and MySQL Servers
Character Strings and Bit Strings
Table Column Types for Different Types of Values
Using DDL to Create Tables and Indexes
Using DML to Insert, Update and Delete Records
Using SELECT to Query Database
Window Functions for Statistical Analysis
Use Index for Better Performance
Transaction Management and Isolation Levels
Defining and Calling Stored Procedures
Variables, Loops and Cursors Used in Stored Procedures
System, User-Defined and Stored Procedure Variables
►Storage Engines in MySQL Server
Convert Table to InnoDB Storage Engine
Clustered Index Used by InnoDB Engine
Statistic Information on InnoDB Tables
MySQL Status Variables for InnoDB Engine
MySQL System Variables for InnoDB Engine
InnoDB Storage Engine - Primary and Secondary Indexes
Performance Tuning and Optimization
Installing MySQL Server on Linux