MySQL Tutorials - Herong's Tutorial Examples - v4.46, by Herong Yang
Clustered Index Used by InnoDB Engine
This section describbes the Clustered Index data structure used by the InnoDB engine to stored indexed data rows of a table in MySQL server.
What Is Clustered Index? A clustered index is a B-Tree (Balanced-Tree) data structure that stores data rows of a table sorted by an index.
In a clustered index, storage spaces are divided into pages, and pages are organized as a balanced tree, where:
- Pages of the root level and intermediate levels in the tree are index pages, which map index ranges sequentially to next level pages.
- Pages of the leaf level in the tree are data pages, which store data rows sequentially according to the index.
According to MySQL reference manual, InnoDB engine stores tables in clustered index structure. It says "Each InnoDB table has a primary key index called the clustered index that organizes the data to minimize I/O for primary key lookups."
It means that each InnoDB table must have a primary key index. If you are not specifying a primary key in your table definition, MySQL will define an internal primary key for you.
For example, let's create a InnoDB table called “Customers” that includes three columns: Customer Number, First Name, and Last Name. The Customer Number column is defined as the primary key:
mysql> CREATE TABLE `Customers` (
-> `CustomerNumber` INT NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
-> `FirstName` VARCHAR(64),
-> `LastName` VARCHAR(64),
-> PRIMARY KEY (`CustomerNumber`)
-> ) ENGINE=MyISAM DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
mysql> show index from Customers;
Table Non_unique Key_name Seq_in_index Column_name Index_type
--------- ---------- -------- ------------ -------------- ----------
Customers 0 PRIMARY 1 CustomerNumber BTREE
The following picture provided by Brad McGehee in "Brad’s Sure Guide to Indexes" at https://www.red-gate.com/simple-talk/databases/sql-server /database-administration-sql-server/brads-sure-guide-to-indexes/ illustrates how this "Customers" will be stored by MySQL server.
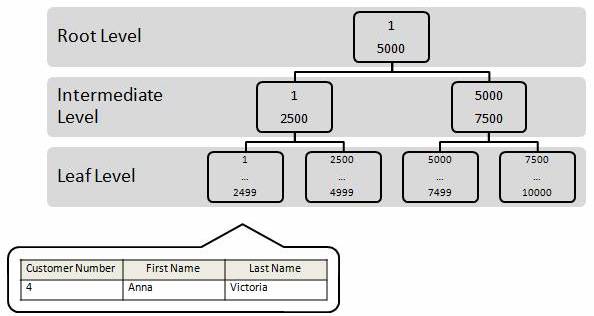
The main advantage of using clustered index is that the data is physically sorted by the index. Retrieving the data row of a given index is very fast.
But to keep the clustered index table effective, you need to remember 4 keywords: Narrow, Unique, Static and Ever Increasing (NUSE), as Michelle Ufford summarized in "Effective Clustered Indexes" at https://www.red-gate.com/simple-talk/databases/sql-server/learn /effective-clustered-indexes/.
- Narrow - The index should be as narrow as possible, in terms of its storage size. A narrower index results in more records in index pages and less levels in the B-Tree structure.
- Unique - The index should be unique to avoid MySQL adding internal row identifier for sorting.
- Static - The index should be static to avoid page relocation.
- Ever-increasing - Index values should increase only for new rows. Delete and insert index values will cause page fragmentation.
Table of Contents
MySQL Introduction and Installation
Introduction of MySQL Programs
Perl Programs and MySQL Servers
Java Programs and MySQL Servers
Character Strings and Bit Strings
Table Column Types for Different Types of Values
Using DDL to Create Tables and Indexes
Using DML to Insert, Update and Delete Records
Using SELECT to Query Database
Window Functions for Statistical Analysis
Use Index for Better Performance
Transaction Management and Isolation Levels
Defining and Calling Stored Procedures
Variables, Loops and Cursors Used in Stored Procedures
System, User-Defined and Stored Procedure Variables
►Storage Engines in MySQL Server
Convert Table to InnoDB Storage Engine
►Clustered Index Used by InnoDB Engine
Statistic Information on InnoDB Tables
MySQL Status Variables for InnoDB Engine
MySQL System Variables for InnoDB Engine
InnoDB Storage Engine - Primary and Secondary Indexes
Performance Tuning and Optimization
Installing MySQL Server on Linux