Molecule Tutorials - Herong's Tutorial Examples - v1.26, by Herong Yang
What Is RNA (Ribonucleic Acid)
This section provides a quick introduction of RNA (Ribonucleic Acid), which a special nucleic acid, which only uses riboses as 5-carbon sugars and 4 primary nucleobases: Adenosine (A), Cytidine (C), Guanosine (G) and Uridine (U).
What Is RNA (Ribonucleic Acid)? - A RNA (Ribonucleic Acid) is a special nucleic acid, which only uses riboses as 5-carbon sugars and 4 primary nucleobases: Adenosine (A), Cytidine (C), Guanosine (G) and Uridine (U).
The picture below shows a section of 4 nucleotide residues of a RNA (source: scienceprofonline.com):
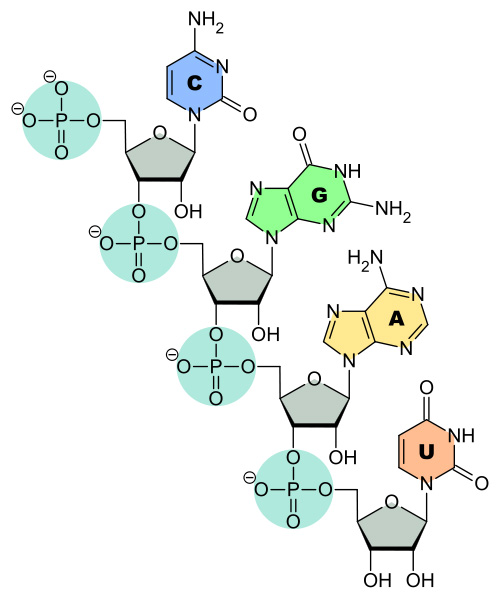
Table of Contents
Molecule Names and Identifications
►Nucleobase, Nucleoside, Nucleotide, DNA and RNA
►What Is RNA (Ribonucleic Acid)
What Is DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid)
DNA Primary Structure - Double Helix
What Is DNA/RNA Base and Sequence Pair
ChEMBL Database - European Molecular Biology Laboratory
PubChem Database - National Library of Medicine
INSDC (International Nucleotide Sequence Database Collaboration)
HGNC (HUGO Gene Nomenclature Committee)