JVM Tutorials - Herong's Tutorial Examples - Version 4.23, by Dr. Herong Yang
Serial, Parallel, Concurrent, and Regionalized Collectors
This section describes different types garbage collectors supported in HotSpot JVM: Serial Collector, Parallel Collector, Parallel Compacting Collector, Concurrent Mark-Sweep Collector, and Garbage First Collector.
HotSpot JVM also offers variations of the Serial Collector, which could be more efficient based the type of your Java application and the computer system you are using:
1. Serial Collector (invoked by "-XX:+UseSerialGC" option) - GC operation is performed serially using 1 CPU only in a stop-the-world fashion for Minor GC and Full GC. Minor GC uses the 3-area (Eden, Survivor Space "From" and Survivor Space "To") algorithm. Full GC uses the 3-step (Mark, Sweep and Compact) algorithm.
2. Parallel Collector (also called Throughput Collector, invoked by "-XX:+UseParallelGC" option) - Minor GC uses multiple CPUs and Full GC uses 1 CPU. Both Minor GC and Full GC are done in a stop-the-world fashion and same algorithms as the Serial Collector.
3. Parallel Compacting Collector (invoked by "-XX:+UseParallelOldGC" option) - Minor GC is done in the same way as the Parallel Collector. Full GC is done in a stop-the-world fashion but using multiple CPUs most of the time.
4. Concurrent Mark-Sweep (CMS) Collector (also called Low-Latency Collector, invoked by "-XX:+UseConcMarkSweepGC" option) - Minor GC is done in the same way as the Parallel Collector. Full GC is done concurrently with the execution of the Java application nost of the time.
5. Garbage First (G1) Collector (invoked by "-XX:+UseG1GC" option) - The Garbage First (G1) Collector is a regionalized and generational garbage collector. The Heap area is first divided into a number of equally sized regions. Then sets of regions are picked up to form the Eden, Survivor Space "From", Survivor Space "To" and Tenured Generation spaces. This region concept allows Garbage First Collector to measure how much garbage each region has, and to collect garbage in regions mostly filled with garbage first. This is why it is called "Garbage First". When performing garbage collection in a region, The Garbage First Collector follows an algorithm similar to the Concurrent Mark-Sweep Collector.
The table below summarizes all 4 garbage collectors supported in HotSpot:
GC Variations Minor GC Full GC CPU
------------- -------- ------- ---
Serial Collector Serial Serial 1
-XX:+UseSerialGC Stop-the-world Stop-the-world
Parallel Collector Mostly Parallel Serial Multi
Throughput Collector Stop-the-world Stop-the-world
-XX:+UseParallelGC
Parallel Compacting Mostly Parallel Mostly Parallel Multi
-XX:+UseParallelOldGC Stop-the-world Stop-the-world
Concurrent Mark-Sweep Mostly Parallel Mostly Parallel Multi
CMS Collector Stop-the-world Mostly concurrent
Low-Latency Collector
-XX:+UseConcMarkSweepGC
Garbage First (G1) Mostly Parallel Mostly Parallel Multi
-XX:+UseG1GC Stop-the-world Mostly concurrent
Today most computers have multiple CPUs. So the best option for majority of Java application is to use the Parallel Compacting Collector, which gives the most throughput in terms of application execution time over GC time.
If your application requires fast response time, then you should use the G1 Collector, which gives the least and predictable GC pauses.
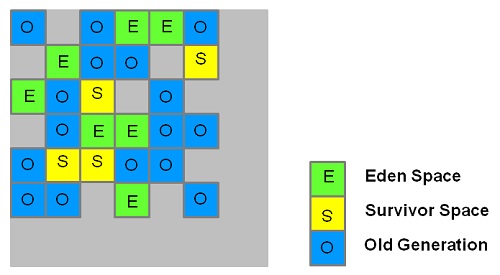
The picture below shows how the Heap area is divided into regions and how regions are assigned to
Eden, Survivor Spaces ("From" and "To"), and Tenured (Old) Generation:
Last update: 2014.
Table of Contents
Downloading and Installing JDK 1.8.0 on Windows
Downloading and Installing JDK 1.7.0 on Windows
java.lang.Runtime Class - The JVM Instance
java.lang.System Class - The Operating System
ClassLoader Class - Class Loaders
Class Class - Class Reflections
JRockit JVM 28.2.7 by Oracle Corporation
►Memory Management and Garbage Collectors
Memory Management General Rules
Java Exception: "java.lang.OutOfMemoryError: Java heap space"
OutOfMemoryError Comparison of HotSpot and JRockit
Garbage Collection Demonstration
JVM Memory Manager - Garbage Collector
Generational Garbage Collection in HotSpot
Young Generation Collection - Minor Collection
Tenured Generation Collection - Full Collection
HotSpot Default Garbage Collector - Serial Collector
"-XX:+PrintGCDetails" - Garbage Collection Logging
GC Log Messages on GarbageCollection.java
►Serial, Parallel, Concurrent, and Regionalized Collectors
Parallel Collector GC Log Message Format
Parallel Compacting Collector GC Log Message Format
Concurrent Mark-Sweep Collector GC Log Message Format
Garbage First GC Log Message Format
JVM Stack, Frame and Stack Overflow
Thread Testing Program and Result
CPU Impact of Multi-Thread Applications
I/O Impact of Multi-Thread Applications
Micro Benchmark Runner and JVM Options
Micro Benchmark Tests on "int" Operations
Micro Benchmark Tests on "long" Operations
Micro Benchmark Tests in JIT Compilation Mode