Java Tutorials - Herong's Tutorial Examples - v8.22, by Herong Yang
Class and Interface Hierarchy
This section describes Java class and interface hierarchical relationships to support object inheritance: superclass-subclass relation, superinteface-subinterface relation, and interface-class relation.
Java allows classes and interfaces to be created with hierarchical relationship to support object inheritance. The class and interface hierarchy supports 3 types of relations:
1. Superclass-Subclass Relation - The subclass extends the superclass and inherits all behaviors of the superclass. An example is listed below:
class javax.net.ssl.X509ExtendedKeyManager
extends java.lang.Object {};
// superclass: java.lang.Object
// subclass: javax.net.ssl.X509ExtendedKeyManager
2. Superinteface-Subinterface Relation - The subinterface extends the superinterface and inherits all behaviors of the superinterface. An example is listed below:
interface javax.net.ssl.X509KeyManager
extends javax.net.ssl.KeyManager {};
// superinterface: javax.net.ssl.KeyManager
// subinterface: javax.net.ssl.X509KeyManager
3. Interface-Class Relation - The class implements the interface and inherits all behaviors of the interface. An example is listed below:
class javax.net.ssl.X509ExtendedKeyManager
implements javax.net.ssl.X509KeyManager {};
// interface: javax.net.ssl.X509KeyManager
// class: javax.net.ssl.X509ExtendedKeyManager
The diagram below shows you a simple class interface hierarchy example:
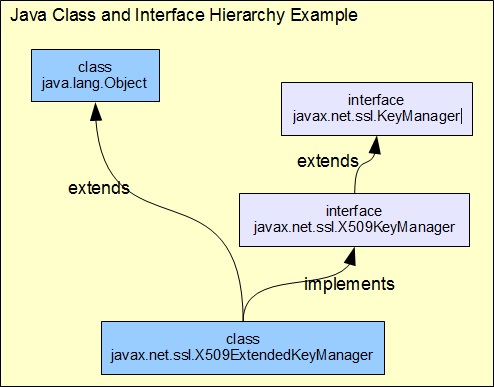
By default, all classes extend the java.lang.Object class. In other words, all classes are subclasses of the java.lang.Object class.
Table of Contents
Execution Process, Entry Point, Input and Output
Primitive Data Types and Literals
Bits, Bytes, Bitwise and Shift Operations
Managing Bit Strings in Byte Arrays
►Reference Data Types and Variables
Reference Types Supported in Java
Class Type Variables Storing References
►Class and Interface Hierarchy
Explicit and Implicit Type Casting
Type Casting Compile and Runtime Error
StringBuffer - The String Buffer Class
System Properties and Runtime Object Methods
Generic Classes and Parameterized Types
Generic Methods and Type Inference
Lambda Expressions and Method References
Java Modules - Java Package Aggregation
Execution Threads and Multi-Threading Java Programs
ThreadGroup Class and "system" ThreadGroup Tree
Synchronization Technique and Synchronized Code Blocks
Deadlock Condition Example Programs
Garbage Collection and the gc() Method
Assert Statements and -ea" Option