Email Tutorials - Herong's Tutorial Examples - v1.04, by Herong Yang
What Is Email
This section provides a quick introduction on email and how email messages are processed by 4 types of software agents: MUA, MSA, MTA, and MDA.
What Is Email? - Email, or E-Mail, (Electronic Mail) is a computer communication technology that allows users to send and receive messages to each other on their electronic devices.
In 1971, the first email with an address format of user@host was sent on the ARPANET network mail was sent.
In 1981, Jonathan B. Postel published "RFC788 - Simple Mail Transfer Protocol" ( datatracker.ietf.org/doc/html/rfc788) as the communication protocol of email messages on the Internet.
In 1983, BSD Unix introduced the first mail transfer agent, sendmail, that implements the SMTP (Simple Mail Transfer Protocol). It allows users to send emails on local networks.
Today, users can send emails across different software tools, different devices, and different parts of the world.
There are 4 main software agents involved in the process of submitting, transmitting and delivering emails between users:
- MUA (Message User Agent, or Mail User Agent), also called Email client - A computer program for end users to compose outgoing mail messages and retrieve incoming mail messages. For example, the Email app on your phone is a MUA.
- MSA (Message Submission Agent, or Mail Submission Agent) - A computer program that receives email messages from a MUA and forwards them to a MTA (Message Transfer Agent) for delivery. For example, the Yahoo mail server plays the MSA role, if you are using Yahoo to send a email message.
- MTA (Message Transfer Agent, or Mail Transfer Agent), also called Mail Relay, Mail Exchanger, or MX Host - A computer program that transfers email messages from one computer to another. For example, Postfix is a MTA.
- MDA (Message Delivery Agent, or Mail Delivery Agent), A computer program that is responsible for the delivery of email messages to local recipient's mailboxes.
The following diagram shows you how those software agents works to together to submit, transmit and deliver emails between users. Communication protocols between processing agents are also included.
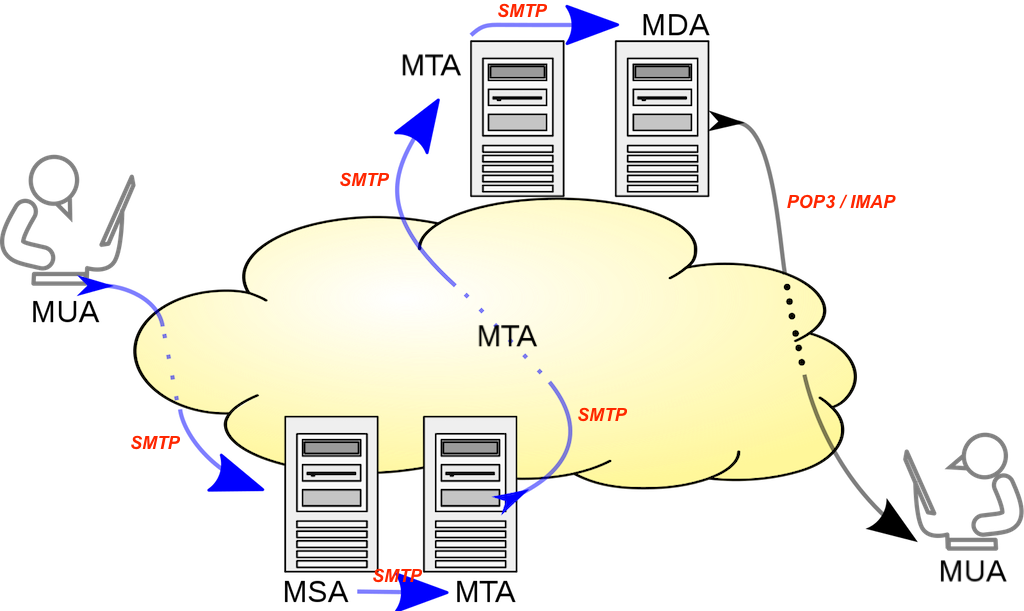
Table of Contents
Postfix - Mail Transport Agent (MTA)
SSL/TLS Secure Connections with Postfix Server
Dovecot - IMAP and POP3 Server
SSL/TLS Secure Connections with Dovecot Server
Email Client Tools - Mail User Agents (MUA)
Mozilla Thunderbird - Mail User Agents (MUA)
PHPMailer - PHP Package for Sending Emails