Physics Notes - Herong's Tutorial Notes - v3.25, by Herong Yang
Measuring Speed of Light - Foucault's Method
This section describes the method used by Léon Foucault to measure the speed of light using using a rotating mirror and a fixed mirror.
In 1857, the French physicist Léon Foucault enhanced Fizeau method to measure the speed of light using a rotating mirror and a fixed mirror, as illustrated in the picture below.
Foucault's measurement is based on the following idea:
- Light coming from the source hits a rotating mirror.
- The rotating mirror reflects the light to a fixed mirror at a far distance (like 8,000 m).
- Then fixed mirror the light back to rotating mirror.
- This backward light will be bounded off the rotating mirror towards the light source with a small angle caused by the rotation. This angle can be used calculate the speed of light.
Using this idea, Foucault was able to measure the speed of light as 299,796,000 m/s. This is very close to today's definition of the speed of light: 299,792,458 m/s.
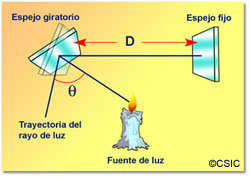
Table of Contents
Introduction of Frame of Reference
Different Speeds Observed in Different Frames
Measuring Speed of Light - Roemer's Method
Measuring Speed of Light - Fizeau's Method
►Measuring Speed of Light - Foucault's Method
Introduction of Special Relativity
Time Dilation in Special Relativity
Length Contraction in Special Relativity
The Relativity of Simultaneity
Minkowski Spacetime and Diagrams
Introduction of Generalized Coordinates