Physics Notes - Herong's Tutorial Notes - v3.25, by Herong Yang
Newton's Third Law of Motion
This section introduces Newton's Third Law of Motion - If a force is exerted by one object to another object, another force is simultaneously exerted by the second object to the first object with equal strength and opposite direction.
Newton's Third Law of Motion - If a force is exerted by one object to another object, another force is simultaneously exerted by the second object to the first object with equal strength and opposite direction.
For example, when you push the water backward with a force, F, with a paddle, the water will push you forward with an opposite force, F' = -F. Under the force F, some water will move backward. And under the force F', you and your canoe will move forward.
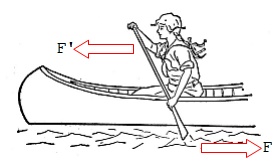
Table of Contents
Introduction of Frame of Reference
Falling Ball in Earth Frame of Reference
Falling Ball in Elevator Frame of Reference
Introduction of Special Relativity
Time Dilation in Special Relativity
Length Contraction in Special Relativity
The Relativity of Simultaneity
Minkowski Spacetime and Diagrams
Introduction of Generalized Coordinates