PKI Tutorials - Herong's Tutorial Examples - v2.32, by Herong Yang
Viewing Certificate Properties and Purposes
This section provides a tutorial example on how to view certificate properties and purposes using the certificates console on a Windows system.
View the Certificates console, you can also view and change properties of a root CA certificates:
1. Click "Start > All Programs > Administrative Tools > MyCertificatesConsole.msc". "MyCertificatesConsole" window shows up.
2. Open "Certificates (Local Computer) > Trusted Root Certification Authorities > Certificates" in the Console Root tree. A list of all certificates in "Trusted Root Certification Authorities" store shows up.
3. Select "Go Daddy Class 2 Certification Authority" and click "Properties" from the "Action" menu. The properties dialog box shows up:
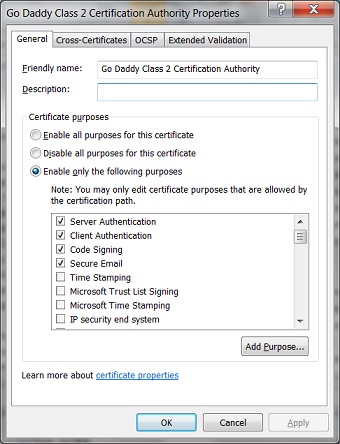
4. On the "General" tab, you can see options for "Certificate purposes" listed as:
() Enable all purposes for this certificate () Disable all purposes for this certificate () Enable only the following purposes: [x] Server Authentication [x] Client Authentication [x] Code Signing [x] Secure Email [ ] Time Stamping [ ] Microsoft Trust List Signing [ ] Microsoft Time Stamping [ ] IP security end system [ ] IP security tunnel termination [ ] IP security user [ ] Encrypting File System [ ] Windows Hardware Driver Verification [ ] Windows System Component Verification [ ] OEM Windows System Component Verification [ ] Embedded Windows System Component Verification [ ] Key Pack Licenses [ ] License Server Verification [ ] Smart Card Logon [ ] Digital Rights [ ] Qualified Subordination [ ] Key Recovery [ ] Document Signing [ ] IP security IKE intermediate [ ] File Recovery [ ] Root List Signer [ ] All application policies [ ] Directory Service Email Replication [ ] Certificate Request Agent [ ] Key Recovery Agent [ ] CA Encryption Certificate [ ] Lifetime Signing
Very interesting to see that a PKI certificate can be used for so many different purposes.
Table of Contents
Introduction of PKI (Public Key Infrastructure)
Introduction of HTTPS (Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure)
Using HTTPS with Google Chrome
Using HTTPS with Mozilla Firefox
HTTPS with IE (Internet Explorer)
Android and Server Certificate
►Windows Certificate Stores and Console
Microsoft Management Console (MMC)
Creating Certificate Console as a MMC Snap-In
Exporting a List of Root CA Certificates
►Viewing Certificate Properties and Purposes
Exporting a Root CA Certificate to a File
Deleting a Root CA Certificate
Importing a Root CA Certificate from a File
Disabling a Root CA Certificate
RDP (Remote Desktop Protocol) and Server Certificate
macOS Certificate Stores and Keychain Access
Perl Scripts Communicating with HTTPS Servers
PHP Scripts Communicating with HTTPS Servers
Java Programs Communicating with HTTPS Servers
.NET Programs Communicating with HTTPS Servers
CAcert.org - Root CA Offering Free Certificates
PKI CA Administration - Issuing Certificates
Comodo Free Personal Certificate
Digital Signature - Microsoft Word
Digital Signature - OpenOffice.org 3