Physics Notes - Herong's Tutorial Notes - v3.25, by Herong Yang
Moving Frames and Galilean Transformation
This section provides a quick introduction of the Galilean transformation between two frames that are move relative to each other.
In previous sections, we learned how to setup a spacetime coordinate system for a single reference frame. Now let's look at how to setup spacetime coordinate systems for two reference frames.
A simple case of two reference frames is that one frame is relatively moving from other frame at a constant speed. Here is a thought experiment example:
- Bob on the ground uses the ground as his spacetime frame (x,t), where x is the space coordinate and t is the time coordinate. In order to simplify the discussion, only 1-dimension space is considered.
- Amy on a moving train uses the train as her spacetime frame (x',t'), where x' is the space coordinate and t' is the time coordinate.
- The origin of (x',t') is adjusted to be at the same spacetime location as the origin of (x,t).
- The train is moving at a constant speed of v relative to the ground.
Now let's ask a simple question. If we consider a stationary object O on the ground, Bob observes (X,T) as the coordinates of object O at time T in his stationary frame, while Amy observes (X',T') as the coordinates of the same object at the same moment in her moving frame, what would be the relation between (X,T) and (X',T')?
The answer is also simple in Newtonian physics:
T' = T # time is an invariant X' = X - v*T # Galilean transformation
As you can see, the Galilean transformation formula perfectly matches assumptions used in Newtonian physics, in which time passes by at the same rate in all frames and spacial coordinates are linearly related to each other between any two frames.
The above thought experiment can be easily presented in two separated diagrams shown below. One represents Bob's stationary frame. And the other represents Amy's moving frame.
Notice that in Bob's frame, the world line of Bob follows the t axis assuming that he stays at x=0. The world line of object O is vertical line at x=X. The world line of Amy is diagonal line starting from the origin, assuming she is there at t=0.
In Amy's frame, the world line of Amy follows the t' axis. World lines of object O and Bob are moving backward.
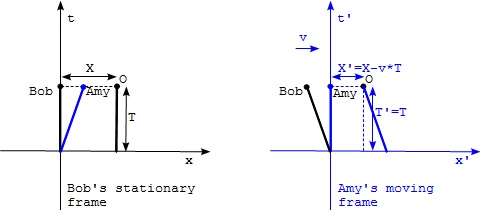
Table of Contents
Introduction of Frame of Reference
Introduction of Special Relativity
Time Dilation in Special Relativity
Length Contraction in Special Relativity
The Relativity of Simultaneity
►Moving Frames and Galilean Transformation
Galilean Diagram of Moving Frames
Minkowski Spacetime and Diagrams
Introduction of Generalized Coordinates