Physics Notes - Herong's Tutorial Notes - v3.25, by Herong Yang
Galilean Diagram of Moving Frames
This section presents a single diagram that represents a moving frame overlaid on a stationary frame. The time axis of the moving frame is rotated towards the moving direction.
In previous section, we presented Bob's frame and Amy's frame as separate diagrams. We can also overlay both frames in a single diagram and keep the current location of object O overlapped as a single point:
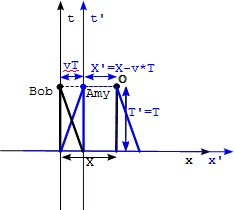
In the above diagram, coordinates of both frames are maintained as orthogonal coordinate systems. The origin of the Amy's frame in blue color is moving at a speed of v. The Galilean transformation is clearly presented by looking at the difference of distances from object O to t axis and t' axis.
However, world lines of Amy, Bob and object O are presented with different lines for different frames. We can also revise the diagram to simplify those world lines by:
- Keeping origins of both frames overlapped as a single point all the time.
- Rotating t' axis to match the world line of Amy in Bob's frame.
- Rescaling t' axis so that t' equals to the t if they are at the same horizontal level.
- Keeping x' axis as is.

As you can see, now world lines of Amy, Bob and object O are perfectly identical in both frames. The Galilean transformation between two frames is clearly presented in a single simple diagram. Let's call it Galilean diagram.
The only downside of the Galilean diagram is that t' axis is no longer orthogonal to x' and t' has a different scale than t.
To determine the coordinates (X',T') of an event in (x',t') frame, we have to:
- Draw a line parallel to t' and passing through the event. The intersection point of this line on the x' axis is the reading of X'.
- Draw a line parallel to x' and passing through the event. The intersection point of this line on the t axis is the reading of T'.
Table of Contents
Introduction of Frame of Reference
Introduction of Special Relativity
Time Dilation in Special Relativity
Length Contraction in Special Relativity
The Relativity of Simultaneity
Moving Frames and Galilean Transformation
►Galilean Diagram of Moving Frames
Minkowski Spacetime and Diagrams
Introduction of Generalized Coordinates