Java Swing Tutorials - Herong's Tutorial Examples - v4.32, by Herong Yang
LookAndFeel and UIManager
This chapter provides tutorial notes and example codes on UI look and feel. Topics include introduction of javax.swing.LookAndFeel and javax.swing.UIManager classes; example programs on how to manage UI look and feel.
javax.swing.LookAndFeel - A Swing class representing a set of rules that define how each type of graphical components should look and feel.
javax.swing.UIManager - A Swing class managing the current LookAndFeel.
To find out which LookAndFeel is available on your local system, and to switch from one LookAndFeel to another, I wrote the following sample program:
/* LookAndFeelTest2.java
* Copyright (c) 1997-2024 HerongYang.com. All Rights Reserved.
*/
import java.awt.*;
import javax.swing.*;
public class LookAndFeelTest2 {
public static void main(String[] a) {
try {
showFrame("Default LookAndFeel", 1);
String cn = UIManager.getSystemLookAndFeelClassName();
UIManager.setLookAndFeel(cn);
showFrame("System LookAndFeel", 2);
cn = UIManager.getCrossPlatformLookAndFeelClassName();
UIManager.setLookAndFeel(cn);
showFrame("Cross Platform LookAndFeel", 3);
cn = "com.sun.java.swing.plaf.motif.MotifLookAndFeel";
UIManager.setLookAndFeel(cn);
showFrame("Motif LookAndFeel", 4);
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("Exception: "+e);
}
}
private static void showFrame(String t, int i) {
LookAndFeel laf = UIManager.getLookAndFeel();
JFrame myFrame = new JFrame(i+". "+t+": "+laf.getName());
myFrame.setBounds(50*i,50*i,0,0);
myFrame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
Container myPane = myFrame.getContentPane();
myPane.setLayout(new GridBagLayout());
GridBagConstraints c = new GridBagConstraints();
setMyConstraints(c,0,0,GridBagConstraints.CENTER);
myPane.add(getFieldPanel(),c);
setMyConstraints(c,0,1,GridBagConstraints.CENTER);
myPane.add(getButtonPanel(),c);
myFrame.pack();
myFrame.setVisible(true);
}
private static JPanel getFieldPanel() {
JPanel p = new JPanel(new GridBagLayout());
p.setBorder(BorderFactory.createTitledBorder("Details"));
GridBagConstraints c = new GridBagConstraints();
setMyConstraints(c,0,0,GridBagConstraints.EAST);
p.add(new JLabel("Name:"),c);
setMyConstraints(c,1,0,GridBagConstraints.WEST);
p.add(new JTextField(16),c);
setMyConstraints(c,0,1,GridBagConstraints.EAST);
p.add(new JLabel("System:"),c);
setMyConstraints(c,1,1,GridBagConstraints.WEST);
p.add(getSystemPanel(),c);
setMyConstraints(c,0,2,GridBagConstraints.EAST);
p.add(new JLabel("Language:"),c);
setMyConstraints(c,1,2,GridBagConstraints.WEST);
p.add(getLanguagePanel(),c);
setMyConstraints(c,0,3,GridBagConstraints.EAST);
p.add(new JLabel("Year:"),c);
setMyConstraints(c,1,3,GridBagConstraints.WEST);
p.add(new JComboBox<String>(
new String[] {"2021","2022","2023"}),c);
return p;
}
private static JPanel getButtonPanel() {
JPanel p = new JPanel(new GridBagLayout());
p.add(new JButton("OK"));
p.add(new JButton("Cancel"));
return p;
}
private static JPanel getSystemPanel() {
JRadioButton unixButton = new JRadioButton("Unix",true);
JRadioButton winButton = new JRadioButton("Window",false);
ButtonGroup systemGroup = new ButtonGroup();
systemGroup.add(unixButton);
systemGroup.add(winButton);
JPanel p = new JPanel(new GridBagLayout());
p.add(unixButton);
p.add(winButton);
return p;
}
private static JPanel getLanguagePanel() {
JPanel p = new JPanel(new GridBagLayout());
p.add(new JCheckBox("Java",true));
p.add(new JCheckBox("C++",true));
p.add(new JCheckBox("Perl",false));
return p;
}
private static void setMyConstraints(GridBagConstraints c,
int gridx, int gridy, int anchor) {
c.gridx = gridx;
c.gridy = gridy;
c.anchor = anchor;
}
}
Run it. You should get 4 windows, representing the JDK default LookAndFeel, the local system default LookAndFeel, cross platform LookAndFeel, and the Motif LookAndFeel.
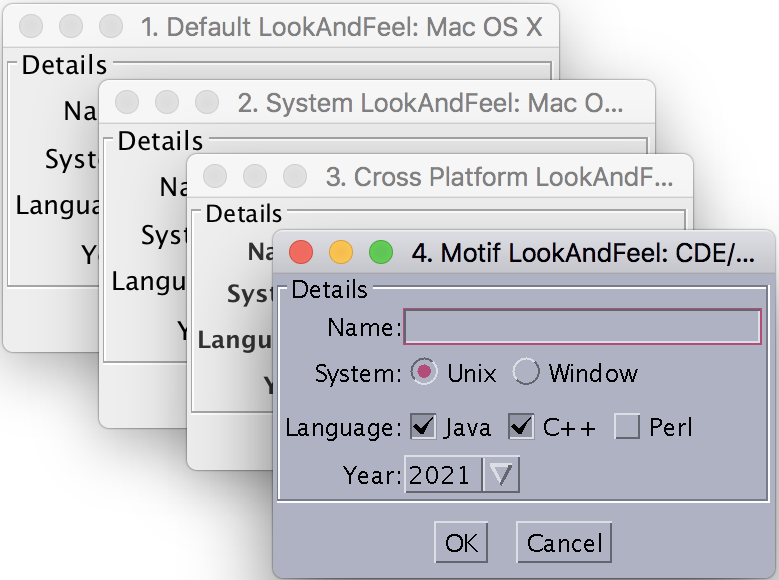
As you can see, the JDK default LookAndFeel is called Metal, which is also the cross platform LookAndFeel.
Sample programs listed in this tutorial have been tested with JDK 1.3.1 to JDK 20 on Windows and macOS computers.
Table of Contents
Introduction of Java Swing Package
Graphics Environment of the Local System
JCheckBox - Swing Check Box Class
JRadioButton - Swing Radio Button Class
JTextField - Swing Text Field Class
JComboBox - Swing Combo Box Class
Menu Bar, Menus, Menu Items and Listeners
Creating Internal Frames inside the Main Frame
Layout of Components in a Container
JEditorPane - The Editor Pane Class
SwingWorker - The Background Task Worker
AWT (Abstract Windows Toolkit)